In industrial production, "mixing" and "granulation" are key links connecting raw material processing and finished product manufacturing. The inclined mixing granulator, with its unique structural design, has become an equipment choice that balances efficiency and quality. To fully leverage its value, it is first necessary to understand its "strengths" at the principle level, and then match its application advantages with specific scenarios.
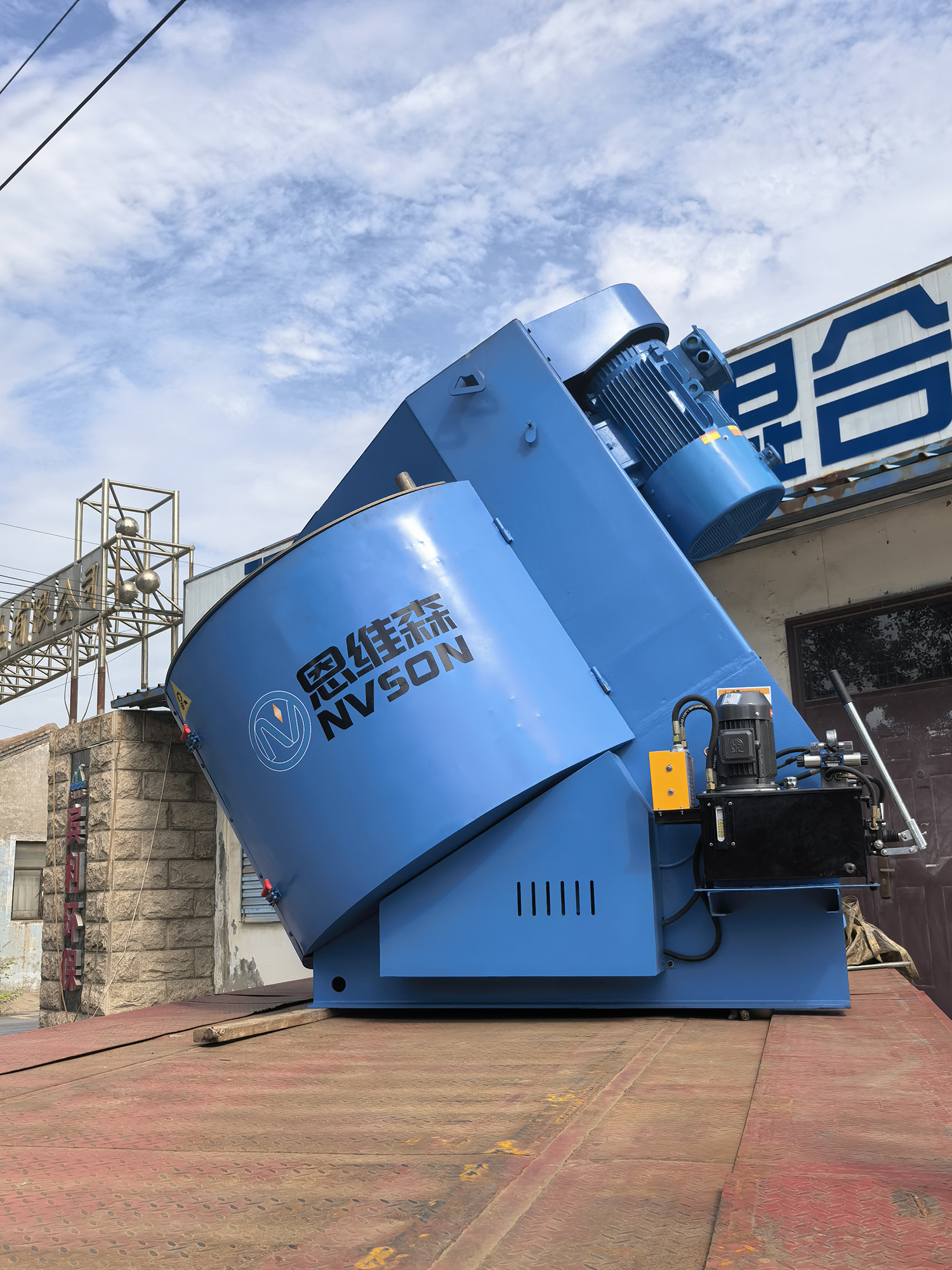
Most traditional granulation equipment adopts vertical or horizontal structures, which often face three major pain points: "uneven mixing", "residues during discharge", and "material wall sticking". The core innovation of the inclined mixing granulator lies in designing the main body of the equipment with an adjustable inclination angle of 30°-45°. Combined with the built-in double-helix stirring paddles and granulation cutters, it forms a working mode of "three-dimensional movement + precise cutting":
Mixing Stage: The inclined machine body enables materials to move circumferentially along the inner wall of the machine under the dual action of gravity and stirring paddles, while also rolling up and down along the inclined direction. This avoids the problems of "material deposition at the bottom" in traditional horizontal equipment and "material sticking to the wall without flowing" in vertical equipment. The mixing uniformity can reach over 95%, making it particularly suitable for powder raw materials with large density differences (such as excipients and active ingredients in the pharmaceutical industry, and fillers and additives in the chemical industry).
Granulation Stage: After the materials are mixed to a uniform state, the built-in cutters operate synchronously with the stirring paddles to precisely cut the agglomerated materials according to the preset particle size. At the same time, the inclination angle can help adjust the residence time of materials in the machine, avoiding excessively fine or coarse particles and solving the problem of "large particle size deviation" in traditional equipment.
Discharge Stage: The inclined structure allows the finished particles to be discharged quickly by gravity alone without additional pushing devices. The discharge residue is less than 1%, which not only reduces raw material waste but also lowers the difficulty of subsequent cleaning. It is especially suitable for production scenarios that require frequent material replacement.
Based on the principle advantages of the inclined design, this type of equipment also demonstrates three core values in practical applications, becoming a "preferred equipment" in multiple industries:
Strong Compatibility: Whether it is powdery, flocculent, or slightly wet materials, they can be adapted by adjusting the inclination angle and stirring speed without replacing special accessories. For example, in the food industry, it can process raw materials such as milk powder and meal replacement powder; in the chemical industry, it can handle chemical fertilizers, coating powders; and in the pharmaceutical industry, it can process traditional Chinese medicine extract powders, truly realizing "one machine for multiple uses".
Energy Efficiency: Compared with traditional equipment, the inclined structure reduces the friction area between materials and the machine body, lowering the motor load by approximately 20%. At the same time, the integrated "mixing-granulation" process eliminates the need for material transfer, increasing production efficiency by more than 30%, which meets the core demand of "cost reduction and efficiency improvement" in industrial production.
Safety and Stability: The inclination angle of the machine body can be precisely controlled through an intelligent system. Combined with the sealed design, it can not only prevent dust leakage (meeting the hygiene standards of the pharmaceutical and food industries) but also avoid material splashing during high-speed operation, reducing production safety risks.
From principle advantages to practical value, the application scenarios of inclined mixing granulators are highly focused on industries that "have high requirements for mixing uniformity, particle quality, and production flexibility":
Pharmaceutical Industry: Used for granulating raw materials of tablets and capsules, it is necessary to ensure the uniform distribution of active ingredients (to avoid uneven efficacy), and the equipment must meet GMP certification standards. The low-residue and easy-to-clean characteristics of the inclined design exactly meet these needs.
Food Industry: When processing raw materials such as meal replacement powders, solid beverages, and pet food, it is necessary to ensure the uniform mixing of nutritional components and control the particle taste (such as crispness and solubility). The adjustable particle size function of the inclined equipment can accurately meet these requirements.
Chemical Industry: Suitable for granulating chemical fertilizers, coatings, and plastic additives. When dealing with corrosive or high-viscosity materials, the inclined structure can reduce material wall sticking, lower equipment wear, and improve the dissolution rate or dispersibility of finished particles.
Environmental Protection Industry: In sludge treatment and biomass fuel granulation, the inclined equipment can handle materials with high humidity and high impurities, avoiding the "clogging" problem of traditional equipment and facilitating the resource utilization of solid waste.
The value of the inclined mixing granulator essentially lies in the embodiment of "structural design adapting to process needs". Through the ingenuity of the inclination angle, it breaks the functional limitations of traditional equipment, not only solving the technical pain points of "uneven mixing and imprecise granulation" but also adapting to the production scenarios of multiple industries. For enterprises pursuing efficient, stable, and flexible production, understanding its principles and advantages is essential to better utilize the equipment in production and achieve the goals of "cost reduction, quality improvement, and efficiency enhancement".